Industry 4.0 and Cyber Risk: Security in an Age of Connected Production
In this paper, we examine the modern connected digital supply networks, smart factories, and connected devices, focusing on the unique cyber risks faced by each, we proactively integrate cybersecurity into an overall strategy in the age of Industry 4.0.
In 2009, malware manipulated the speed of centrifuges in a nuclear enrichment plant, causing them to spin out of control.
This malware, now known as Stuxnet, was introduced into stand-alone networks via flash drives, and it autonomously spread across production networks.
Stuxnet’s sophistication serves as a powerful example of cyberattacks’ potential as weapons in the world of connected physical factories.
And the battle is decidedly unbalanced: Organizations must protect a wide swath of technology, while attackers need only pinpoint the weakest link.
It is important, however, that we balance our focus between the external threat landscape and the very real - and typically overlooked - cyber risks created by businesses who are increasingly using smart, connected technologies to innovate, transform, modernize, and otherwise make tactical or strategic business decisions that could result in such risk.
These new and emerging risks should be managed and mitigated.
The increased connectivity of smart machinery, a shift known as Industry 4.0, raises the stakes. Industry 4.0 heralds a new age of connected, smart manufacturing, responsive supply networks, and tailored products and services.
Through its use of smart, autonomous technologies, Industry 4.0 strives to marry the digital world with physical action to drive smart factories and enable advanced manufacturing.
But while it plans to enhance digital capabilities throughout the manufacturing and supply chain processes and drive revolutionary changes to connected devices, it also brings with it new cyber risks for which the industry is unprepared.
Developing a fully integrated strategic approach to cyber risk is fundamental to manufacturing value chains as they marry operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) - the very force driving Industry 4.0.
As threat vectors radically expand with the advent of Industry 4.0, new risks should be considered and addressed. Put simply, the challenge of implementing a secure, vigilant, and resilient cyber risk strategy is different in the age of Industry 4.0.
When supply chains, factories, customers, and operations are connected, the risks posed by cyberthreats become all the greater and potentially farther reaching.
Thinking about how to address cyber risk at the end of the strategic process is simply likely too late. Cybersecurity should become an integral part of the strategy, design, and operations, considered from the beginning of any new connected, Industry 4.0–driven initiative.
In this paper, we examine the modern connected digital supply networks, smart factories, and connected device themselves, focusing on the unique cyber risks faced by each.
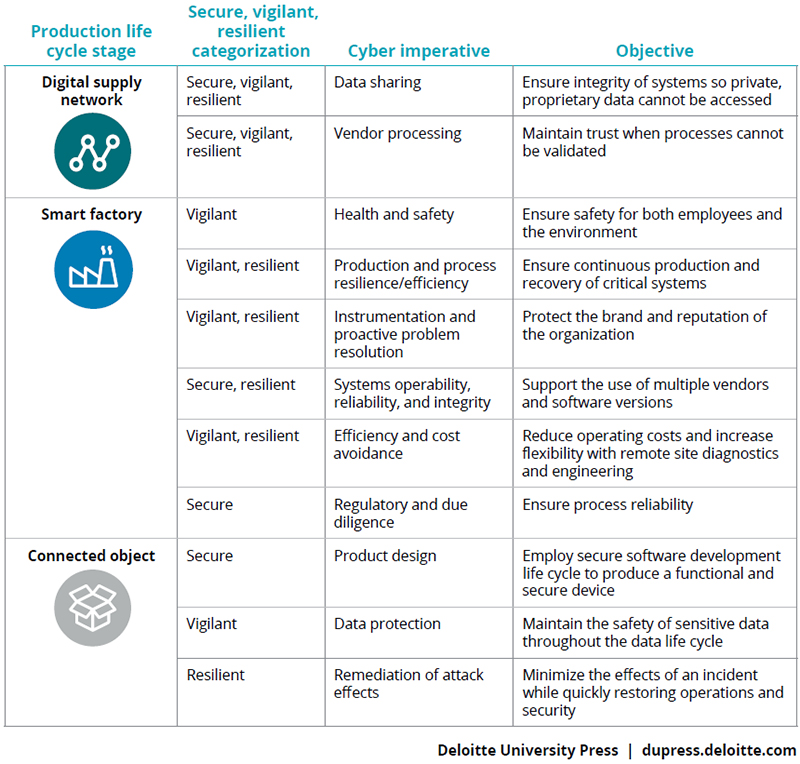
Moving through the production life cycle (figure 1) - from the digital supply network, to the smart factory, and finally to the connected object - we explore the actions operations and information security executives can take to anticipate and effectively address cyber risks as well as proactively integrate cybersecurity into their strategy in the age of Industry 4.0.
Figure 1. Smart production life cycle and cyber risk
What’s Related




Favorites





