Blockchain’s Smart Contracts
ChainsSmart contracts with embedded business rules promise not only to reduce transaction costs but to create more agile value chains that enable closer cooperation and enhanced trust across the extended manufacturing ecosystem.
Blockchain - the cryptocurrency technology with the potential to eliminate financial services intermediaries - may also have the power to fundamentally change the manufacturing industry as we know it.
By allowing supply chain partners to create trusted relationships without the need for banks or, perhaps, even traditional purchasing processes, manufacturers, suppliers, customers and machines can find each other and do business much more quickly and inexpensively.
Even more importantly, they will be able to form more agile supply chains through “smart contracts” that automatically find, negotiate with and close deals with partners the world over.
This will help all participants across the value chain to speed new products to market that meet ever-changing business needs, and will enable more trusted and fruitful relationships.
But leveraging blockchain will require carefully balancing risks versus benefits, integrating new technologies and processes with legacy systems and evaluating the maturity of the required technologies, standards and providers.
It will also require overcoming resistance from both gov-ernment and established intermediaries such as banks.
This white paper explains blockchain, what it means for the manufacturing industry and how to begin using it to drive quantum leaps in efficiency, agility and innovation.
Blockchain Explained
Blockchain is a software mechanism, now primarily known in the form of bitcoin in the financial services world, that provides a distributed system of trusted assets and transactions without the need for a central trust authority.
For manufacturers and their suppliers or logistic partners, an individual transaction in a block might contain bills of lading for raw materials or finished goods, proof of the origin, quality or operations performed on a part or instructions for the place and time of a delivery.
In each case, the information could be stored, trusted, shared and changed by the partners without going to the cost, expense and delay of negotiating formal contracts or paperwork such as letters of credit from a bank or a bond for a transportation provider.
Unlike in a traditional supply chain, where these documents and contracts are maintained by eachpartner’s purchasing, accounting or legal department, in a blockchain these elements are stored on many decentralized nodes.
Their privacy and integrity is maintained by “miner-accountants” rather than by a counterparty or a third party such as a bank (see below).
How Blockchain Works
A distributed database running on multiple servers continually checks the security and integrity of each transaction or data entry. Blocks chained by hash values and incentivized proof of work provide a foundation for distributed trust in blockchain.
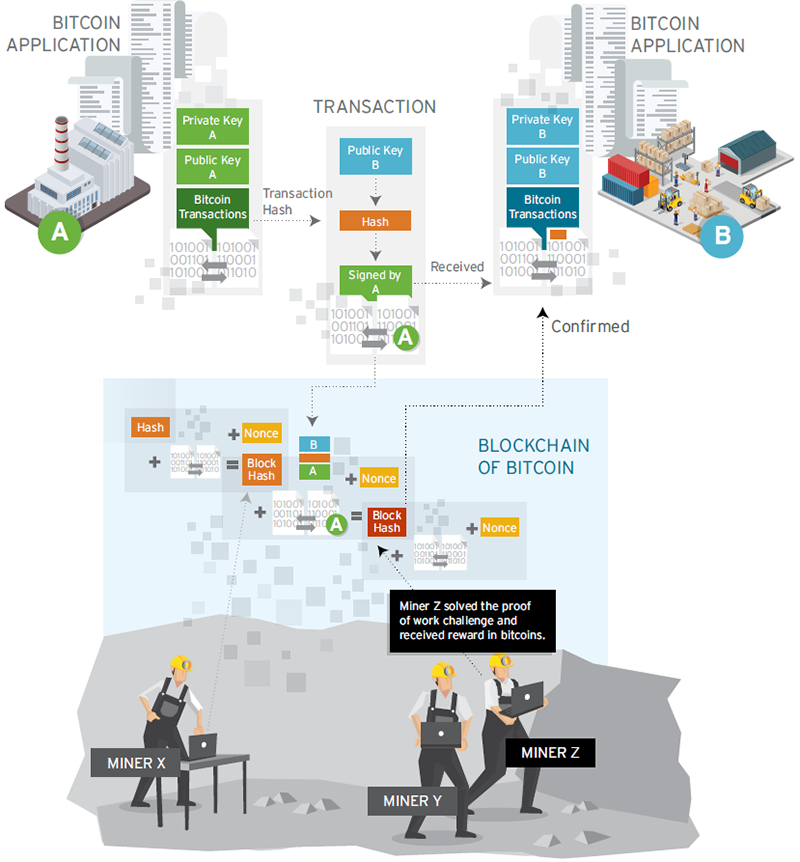
Blockchain enables the creation of smart contracts, with terms and conditions both sides can specify and that assure trust in the enforceability of the contract and the identity of the counterparty.
This system of distributed trust allows for lower transaction costs in the short term, but this is just the beginning. In the long run it will enable more agile value chains, closer cooperation with business partners and faster integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), among other things.
What’s Related




Favorites





