The Economist ‘Imagines’ an Ideological Echo Chamber Email from Larry Page to James Damore

Last week The Economist said Alphabet’s Larry Page should write a “detailed, ringing rebuttal” of the viral anti-diversity memo sent by ex Google employee James Damore regarding Google’s Ideological Echo Chamber, here's how they imagine it.
Created on: 15th August 2017 at 15:15 (Delivered after 1 seconds)
From: Larry Page <*********@google.com>
To: James Damore <***********@hotmail.com>
cc: <[email protected]>
Subject: Re: “Google’s Ideological Echo Chamber”
Dear James,
You’re probably expecting me to start by claiming that there are no differences in the average abilities, aptitudes, and interests of men and women. Or that the fact that four times as many of Google’s software engineers are men than are women is proof of discrimination. I’m not going to do that. There is good evidence for dozens of such differences between the average man and average woman. And as a matter of pure logic, you are correct that the gender gap in our team of software engineers is not of itself proof of sexism or discrimination.
I am happy to acknowledge that you state your support for gender diversity and fairness. Your memo starts: “I value diversity and inclusion, am not denying that sexism exists, and don’t endorse using stereotypes.”
So, you and anyone else who reads this may be wondering, why the fuss? Why did your memo go viral? Why did it cause such fury? Why did we fire you? In interviews and an op-ed in the Wall Street Journal, you have said it’s because Google is “ideologically driven and intolerant of scientific debate”, and therefore unable to tolerate your “reasoned, well-researched, good-faith argument”. You’ve driven the point home with your “Goolag” T-shirt and new twitter handle, @Fired4Truth. You’re wrong. Your memo was a great example of what’s called “motivated reasoning” - seeking out only the information that supports what you already believe. It was derogatory to women in our industry and elsewhere. Despite your stated support for diversity and fairness, it demonstrated profound prejudice. Your chain of reasoning had so many missing links that it hardly mattered what you based your argument on. We try to hire people who are willing to follow where the facts lead, whatever their preconceptions. In your case, we clearly got it wrong.
Have you ever noticed that no one takes sentences that start “I’m not a racist, but…” at face value? Here’s why, in the words of Jon Snow in “Game of Thrones” (season 7, episode 1). When Sansa Stark tells him: “They respect you, they really do, but…,” Snow laughs and comes back with: “What did father use to say? Everything before the word ‘but’ is horseshit.”
I thought of that line when I read this section in your memo: “Of course, men and women experience bias, tech, and the workplace differently and we should be cognizant of this, but it’s far from the whole story. On average, men and women biologically differ in many ways…” All your comments about valuing diversity and fairness came before that giant “but”. What came after it was a description of a few gender differences, your argument that they explain why so many of our software engineers are men and your complaint that Google’s attempts to change that balance, far from being about fairness to women, amount to anti-male bias. You use the words “discriminate” or “discrimination” 17 times, exclusively to describe men as victims.
Now that we’ve worked out what your memo’s really about, let’s examine its argument. These are the main gender differences you cite: women’s on-average greater interest, compared with men, in people and lesser interest in things; their relatively greater tendency to “empathize” rather than “systematize”, and to be agreeable rather than assertive, and their relatively higher anxiety and lower tolerance for stress.
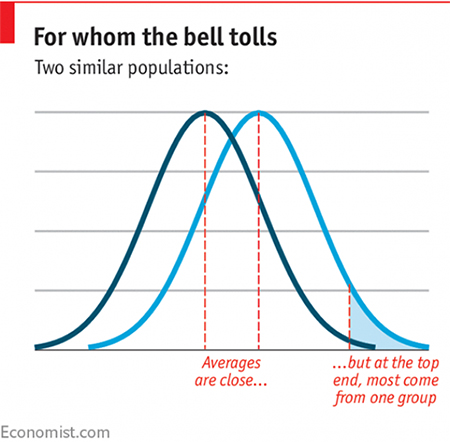
You present a diagram of two normal distributions, with the same standard deviations but slightly different means, to demonstrate that small differences in group averages produce large differences when it comes to outliers. (The Economist’s data team has kindly redrawn this for me, highlighting the “tail” of the distribution with the higher mean.) The point of this simplified model is to demonstrate that, of everyone who scores very highly on the variable under consideration, many more will be from the group with the higher average.
Then you seem to make a giant leap from group differences between men and women on such measures as interest in people rather than things or systematizing versus empathizing, to differences in men’s and women’s ability to code. At least that’s what you seem to be doing; you don’t quite say so. There is no evidence for such an inference. And that is only the first flaw in your argument. I can see at least six more, any of which would derail it on its own.
First, you ignore many other gender differences, basing your argument only on a few that you think support your conclusion. Second, you’re ignoring everything else that could explain the gender gap. Third, the gender differences you cite differ between countries and over time. Fourth, they don’t even support your argument, because you don’t seem to understand what makes a great software engineer. Fifth, you clearly don’t understand our company, and so fail to understand what we are trying to do when we hire. And sixth, even if you are right that more men than women are well-suited to the job of a software engineer at Google, you are wrong that taking steps to recruit more women is inherently unfair to men.
Your memo was a triumph of motivated reasoning: heads men win; tails women lose. Here are a few psychological differences between the sexes that you didn’t mention. Men score higher on measures of anger and lower on cooperation and self-discipline. If it had been the other way round, I’m betting you would have cited these differences as indicating a lack of suitability for the job of a coder. You lean on measures of interest and personality, rather than ability and achievement, presumably because the latter doesn't support your hypothesis. In many countries girls now do better in pretty much every subject at school than boys - again, if it had been the other way around I’m sure you wouldn’t have neglected to mention that fact. The solely published comparison of actual competency in coding I am aware of found that women were more likely than men to have their GitHub contributions accepted - but if they were project outsiders, this was true only if their gender was concealed.
There is plenty of evidence that women in Silicon Valley suffer harassment and discrimination. Read Susan Fowler’s description of the harassment she experienced at Uber before leaving the firm in December. Look at the responses to “Elephant in the Valley”, a recent survey of senior women in tech: among its findings was that two-thirds had been excluded from networking opportunities because of their sex. And beyond our industry, women are less likely to be given plum assignments, are given less useful feedback, are seen as pushy when they ask for pay rises (men are seen as ambitious) and, in leadership roles, may be seen as either competent or likable, but rarely both. “We need to stop assuming that gender gaps imply sexism,” you write. But we know there is sexism! We don’t need to infer it from the existence of gender gaps.
It is more than likely that some psychological differences between men and women have been baked in by evolution, as you note. We see such differences, in varying degrees, in pretty much every animal. With humans, though, you must take great care before concluding that any specific difference is innate since our societies are so much more complex and varied than those of other animals. (By the way, I find it blackly funny that some of the conservatives who have seized on you as a hero don’t believe in evolution at all.)
Here are some reasons to be doubtful about evolutionary basis for the specific differences you cite. Before the 1980s, when personal computers became more common and were almost exclusively marketed to men and boys, a much bigger share of those studying computer science at a university were girls. The share of computer scientists who are women varies wildly from country to country. Even personality differences vary from time to time and place to place - for example, men are more agreeable (the term used by psychologists for a cluster of traits such as modesty, altruism, and tender-mindedness), and less ambitious and status-seeking, in more hierarchical countries. That suggests that at least some of the gaps we see in America are because women are still relatively powerless - just as most men are in more traditional societies. Moreover, those supposedly “female” traits vanish in the rare arenas where the competition is entirely among women. Sopranos and ballerinas are hardly famous for being indifferent about who gets top billing.
I said you didn’t understand what made a great software engineer. If we were talking about weight-lifters or contortionists, it would be simple - and your stylized bell-curve diagram would be the whole story. Men are on average so much stronger, and women so much more supple, that almost all the highest performers are from one sex or the other. But few jobs are that one-dimensional. Software engineering requires a broad mix of skills involving both “people” and “things”. Teamwork, in particular, is important - the stereotypical image of the geek working alone in his basement is far from reality. Senior engineers must manage teams - and by your own reasoning that should mean that women, with their greater empathy and interest in people, should be over-represented at that level, compared with their numbers in more junior jobs. That they are not should have given you pause.
Many of the problems in our industry are caused by the sorts of misconceptions about the work that you clearly hold. Failures of teamwork and product testing are part of the reason so many new releases are glitchy, and so many projects run over time and over budget. I can even point you to ways that products fail because too few women have been involved in their development. When Google Plus was launched users had to state their gender to sign up. The intention was to make it easier to send notifications such as “She shared a photo with you.” Presumably, it didn’t occur to anyone involved in development - all of them men - that many women choose to conceal their sex online to cut down on harassment. Such failures matter far beyond our industry because tech increasingly reaches into every aspect of modern life. I don’t want Google to be part of building a virtual world that is a bad fit for a large part of humanity, as office designers, carmakers and pharmaceutical companies already did in the offline world. (Did you know that car seats and office desks are the wrong proportions for most women, or that many drugs in widespread use were only ever tested on men?)
Finally, let’s look at your contention that by trying to recruit more women Google is discriminating against men. You seem to think that if we stopped paying any attention to applicants’ gender when deciding who to hire, we would naturally converge on the “right” share of men and women, that is, the share that matches the distribution of talent in the recruitment pool. I don’t believe that. Some women will be put off applying by the heavily male culture; those doing the hiring will be influenced in their assessment of ability by the stereotypes they’ve formed in it. We should “treat people as individuals, not as just another member of their group,” you write. That is what we are doing! We’re trying to hire the best, aware that there are forces militating against us.
When you first wondered why so few of our software engineers were women, and why we’re trying to hire more and whether that was fair, there were plenty of smart things you could have done. You could have asked some of your female colleagues about their experiences in the industry. You could have looked for evidence that conflicted with your biases (there’s a good search engine you could have used). Here’s a brief reading list for you. At Heterodox Academy, Sean Stevens and Jonathan Haidt have compiled a pretty comprehensive list of psychological differences between the sexes - there are plenty, not all point the same way and there are many caveats. J. Doe, on Medium, has summarized the evidence that women are treated worse in the tech workplace than men. Suzanne Sadedin, an evolutionary biologist, debunks your pop evo-psych on Quora. Yonatan Zunger, a former senior engineer at Google, discusses your misconceptions about our industry on Medium. Claire Cain Miller talks about the damaging myth of the loner genius nerd in the New York Times. In Vox, Cynthia Lee “ladysplains” your errors from the viewpoint of a woman coder.
I shouldn’t have had to write this: I’m busy and a little effort on your part would have made it unnecessary. But I know I have it easy. Women in our industry have to cope with this sort of nonsense all the time.
Yours,
Larry
Source: The Economist
Related Article: Google’s Pioneering Approach to Supplier Diversity
Diversity Matters
McKinsey has been examining diversity in the workplace for several years, our latest report, Diversity Matters, examined proprietary data sets for 366 public companies across a range of industries in Canada, Latin America, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Download Now!
The Business Case for Supply Chain Sustainability Through Strategic Supplier Inclusion
This white paper discusses the competitive advantages of supplier diversity programs, statistics on the growth of woman & minority owned businesses, demographic shifts impacting the supplier and consumer base. Download Now!
Navigating Disruption Without Gender Diversity? Think Again
What is the link between disruption and gender diversity? Innovation, and in our experience, the way to spark innovation is to harness the power of different ideas from diverse groups of people who are supported by an inclusive culture, part of this equation is gender diversity. Download Now!
The Real Effects of Unconscious Bias in the Workplace
HR and talent management professionals can make a positive contribution to their workplaces by rooting out and minimizing the unconscious biases that can undermine diversity efforts and recruiting and retention programs. Download Now!
Article Topics
The Economist Insights News & Resources
Study Shows CFOs Lack Visibility Into Their Organization’s Business Spend Management The Economist ‘Imagines’ an Ideological Echo Chamber Email from Larry Page to James Damore Why Old-Fashioned Manufacturing Jobs Won’t Be Returning to the Western World Global Trade Reacts To Donald Trump’s Stunning Win Terms of Trade: Understanding Trade Dynamics in the U.S. Companies Worldwide are Optimistic about Future Trade Activity with the U.S. Will Disruption Take a Bite Out of Logistics Jobs? More The Economist InsightsLatest in Business
Ranking the Top 20 Women in Supply Chain TIm Cook Says Apple Plans to Increase Investments in Vietnam Amazon Logistics’ Growth Shakes Up Shipping Industry in 2023 Spotlight Startup: Cart.com is Reimagining Logistics Walmart and Swisslog Expand Partnership with New Texas Facility Nissan Channels Tesla With Its Latest Manufacturing Process U.S. Manufacturing Gains Momentum After Another Strong Month More Business